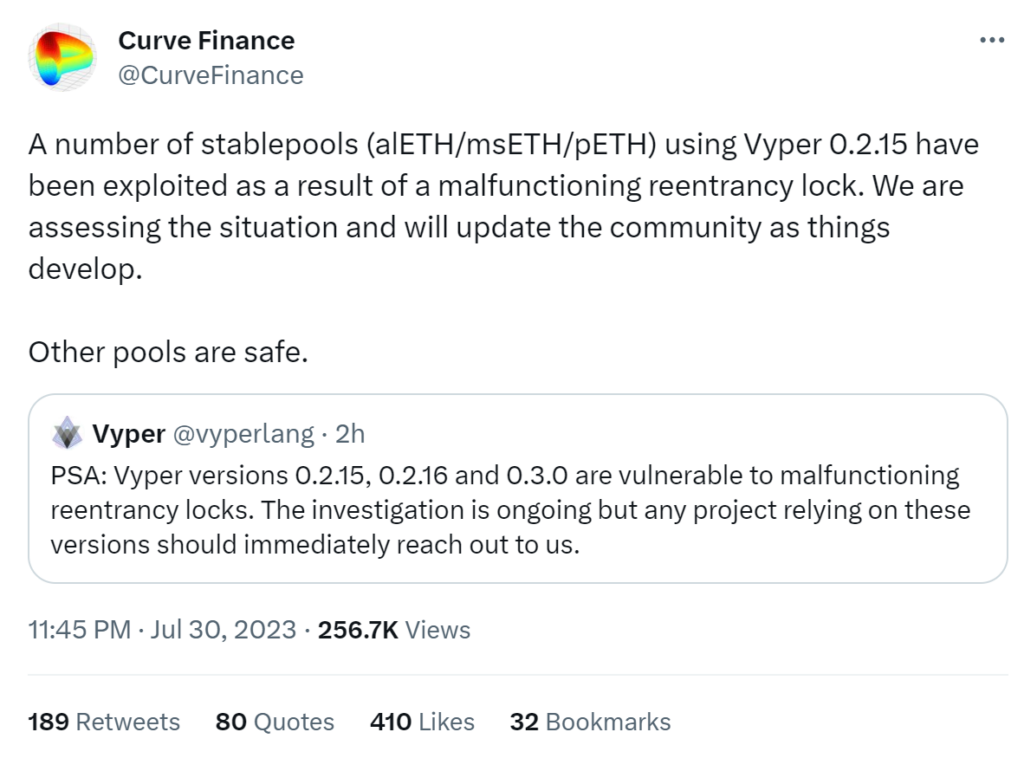
Curve Finance, a decentralized finance (DeFi) protocol that enables the decentralized exchange (DEX) of stablecoins within Ethereum, fell victim to a critical security flaw when multiple factory pools were exploited due to a reentrancy vulnerability. This exploit allowed attackers to interrupt and manipulate external calls, resulting in substantial outflows across associated pools, leading to losses of over $47 million. Projects like JPEGd, Metronome, and Alchemix were affected by the attack.
Vulnerable Factory Pools Witness Significant Outflows
Vyper, a contract-oriented and Pythonic programming language, is specifically designed for the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). Its similarities to Python have made it an attractive choice for developers transitioning into the world of Web3.
Read more: Another Protocol on zkSync Era RugPull: Millions in Losses
The attack had a notable impact on various decentralized finance (DeFi) projects. Ellipsis, a decentralized exchange, reported that a limited number of stable pools with BNB were exploited using an outdated Vyper compiler. Similarly, Alchemix’s alETH-ETH pool experienced an outflow of $13.6 million, while JPEGd’s pETH-ETH pool lost $11.4 million, and Metronome’s sETH-ETH pool saw $1.6 million drained. Michael Egorov, the CEO of Curve Finance, later confirmed in a Telegram channel that the swap pool had lost over $22 million worth of CRV tokens, totaling 32 million tokens. The attack’s impact underscored the vulnerability of certain projects in the DeFi space and the importance of addressing security concerns promptly.
Whitehat Rescue Operation Amidst Panic
As the exploit triggered panic across the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem, data suggested that Miner Extractable Value (MEV) bots might have front-run some of the transactions, leading to speculation about the involvement of whitehat hackers. A security researcher, using the pseudonym ‘pcaversaccio,’ announced a white hat rescue operation on Twitter to aid affected projects.
Vyper acknowledged the vulnerability and urged projects relying on the mentioned versions to get in touch for immediate action. Despite the attack’s impact on the DeFi space and a decline in Curve DAO (CRV) token’s value, the crvUSD contracts and related pools were reported to be unaffected.
Curve Finance Response
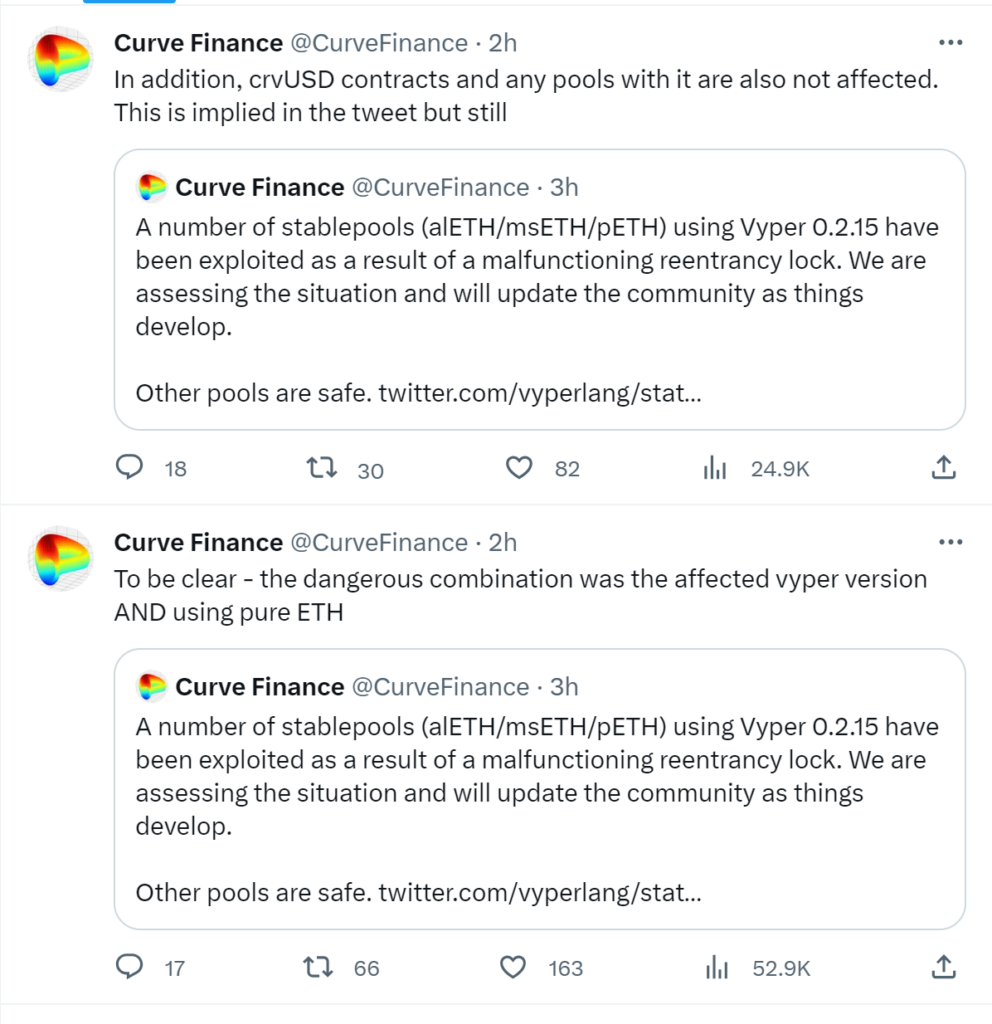
In response to the exploit, Curve Finance issued a clarification, stating that crvUSD contracts and any pools associated with it were not impacted. They emphasized that the dangerous combination that led to the vulnerability was the use of the affected Vyper version in combination with pure ETH.
By providing this information, Curve Finance aimed to reassure its users and the broader community that certain pools were not affected by the security flaw. This clarification was an essential part of their response, as it sought to address concerns and provide transparent information about the extent of the impact on their platform.
Conclusion
The recent reentrancy vulnerability exploit on Curve Finance’s factory pools highlights the ongoing challenges of securing DeFi protocols. The attack resulted in substantial losses, sparking concern and leading to a white hat rescue operation. As the crypto community seeks to safeguard the DeFi ecosystem, it remains crucial for projects and developers to stay vigilant against potential vulnerabilities. The incident also underscores the need for continuous improvements in smart contract programming and thorough security audits to protect user funds and maintain trust in the DeFi space.







![Pionex Review ([currentyear]): Trading Bots, Fees, and Pros & Cons 15 Pionex Review Featured Image](https://coinwire.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/pionex-review-featured-image-1024x683.jpg)